physiotherepy
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
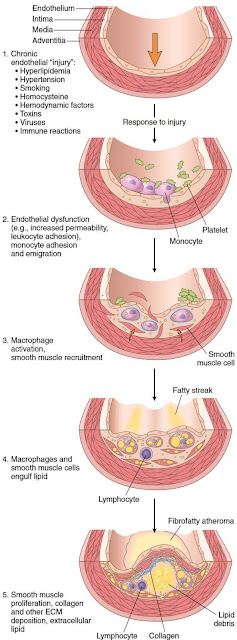
Pathophysiology Of Atherosclerosis
SYMPTOMS
Rest pain: the patient experience pain in bed because when they are lying there would be no gravity . Usually there would be development ofgangrene.
Gangrene: It occurs when tissues receive insufficient blood supply and oxygen , hence causing cell death which becomes black so called Dry gangrene.Intermittent claudication: This is a symptom produced by a significant narrowing of arteries supplying the limbs, most commonly the superficial femoral and the iliac vessels. As the stenosis develops , initially the patient will not develop any symptom. However as stenosis progresses to another site ( such as iliac artery ) , the patient will suffer from calf pain after walking certain distance.
This pain is due to build up of products of anaerobic metabolism in muscles which are starved of oxygen. This pattern of pain which is induced on exercise which and which is relieved by rest is known as intermittent claudication.
Other symptoms: buttock pain
i. Numbness , tingling sensation or weakness in the legs
ii. Loss of hair on the legs. iii. Burning or aching pain in the feet or toes while resting.
iv. Impotence
v. Change in colour ( bluish, pale or dark reddish) of one or both legs.
INVESTIGATION
• Doppler ultrasound – This is the form of ultrasound that can detect and measure blood flow.
This is used to measure blood pressure behind the knees and on the ankles.
In patient with peripheral arterial disease in the legs, the blood pressure in the ankles will be lower than BP in the arms ( brachial blood pressure)
Ankle brachial index Ankle blood pressure Brachial blood pressure
ABI of 9 to 1.3 is normal ; ABI < 0.9 indicate the presence of peripheral artery disease in the legs. ; ABI below 0.5 indicates severe arterial occlusion in the legs.
• Exercise Test: This test is performed by exercising the patient for 5 minutes on a treadmill. Then the ankle brachial pressure index is measured before and after the exercise. A pressure drop of 20% or more indicates disease.
• Auscultation of abdominal aorta , iliac arteries and femoral arteries, down to the popliteal fossa may reveal stenosis.
• Angiography : It is an imaging procedure to study the blood vessels.
This is the test to detect the location and severity of artery occlusion, as well as collateral circulations.
Small hollow plastic tubes(Catheters) are advanced from a small skin puncture at the groin or arm to the aorta and arteries. Iodine contrast dye is then injected into the arteries while recording x-ray video. So that doctors get pictures of the location and severity of narrowed artery segments.
MANAGEMENT
PREVENTIVE MANAGEMENT
The key to reduce risk for atherosclerosis is to reduce the risk factors an individual needs to control over , which includes:
• Eating healthy diet ( low cholesterol and triglycerides) and also fruits and vegetables.
• Body weight
• Stop using tobacco
• Seeking treatment for hypertension
• Proper hygiene
• Activities – patient should be encouraged to exercise frequently.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
• VASODILATORS Like Cinnarizine, Thymoxamine and nicotinic acid derivatives (orally) •ANTICOAGULANTS to prevent arterial thrombus are Heparin and Warfarie.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Treatment include minimally invasive angioplasty procedures that includes physically expanding narrowed arteries and major invasive surgery such as bypass surgery to create additional blood supply connections.
• ANGIOPLASTY AND STENT PLACEMENT
Angioplasty is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. These blood vessels are called the coronary arteries.
The coronary artery stent is a small, metal mesh tube that expands inside a coronary artery. A stent is often placed during or immediately after angioplasty. It helps prevent the artery from closing up again.
Description
Before the angioplasty procedure begins, The patient receives some pain medications. that relaxes them and some blood-thinning medicines to prevent a blood clot from forming.
Patient is instructed to lie on a padded table. The Doctor inserts a flexible tube (catheter) through a surgical cut into an artery. Sometimes the catheter is placed in the arm or wrist, or in the groin area.
The Doctor uses live x-ray pictures to carefully guide the catheter up into the heart and arteries. Dye is injected into the body to highlight blood flows through the arteries. This helps the doctor to see any blockages in the blood vessels that lead to the heart.
A guide wire is moved into and across the blockage. A balloon catheter is pushed over the guide wire and into the blockage. The balloon on the end is blown up (inflated). This opens the blocked vessel and restores proper blood flow to the heart.
A wire mesh tube (stent) may then be placed in this blocked area. The stent is inserted along with the balloon catheter. It expands when the balloon is inflated. The stent is left there to keep the artery open.
The stent may be coated with a drug (called a drug-eluting stent). This type of stent may lower the chance of the artery closing back up in the future. Currently, drug-eluting stents are used only for certain people.
Arteries gets narrowed or blocked by deposits called plaque. Plaque is made up of fat and cholesterol that builds up inside the arterial walls. This condition is called hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis).
Angioplasty may be used to treat :-
-Blockage in a coronary artery during or after a heart attack
-Blockage or narrowing of one or more coronary arteries that may lead to poor heart function (heart failure)
-Narrowing that reduce blood flow and cause persistent chest pain (angina) that medicines do not control.
"Not every blockage can be treated with angioplasty. Some people who have several blockages or blockages in certain locations may need coronary bypass surgery."


Comments
Post a Comment